
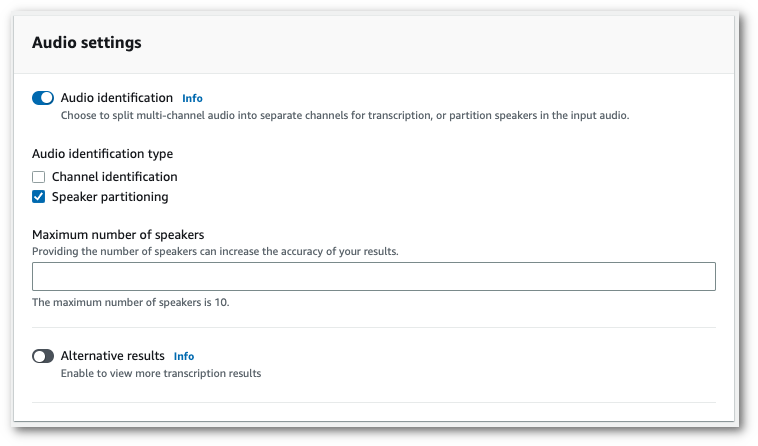
With speaker diarization, you can distinguish between different speakers in your transcription output. Amazon Transcribe can differentiate between a maximum of 30 unique speakers and labels the text from each unique speaker with a unique value ( spk_0 through spk_9 ).
In addition to the standard transcript sections ( transcripts and items ), requests with speaker partitioning enabled include a speaker_labels section. This section is grouped by speaker and contains information on each utterance, including speaker label and timestamps.
"speaker_labels": "channel_label": "ch_0", "speakers": 2, "segments": [ "start_time": "4.87", "speaker_label": "spk_0", "end_time": "6.88", "items": [ "start_time": "4.87", "speaker_label": "spk_0", "end_time": "5.02" >, . "start_time": "8.49", "speaker_label": "spk_1", "end_time": "9.24", "items": [ "start_time": "8.49", "speaker_label": "spk_1", "end_time": "8.88" >,To view a complete example transcript with speaker partitioning (for two speakers), see Example diarization output (batch).
To partition speakers in a batch transcription, see the following examples:

This example uses the start-transcription-job . For more information, see StartTranscriptionJob .
aws transcribe start-transcription-job \ --region us-west-2 \ --transcription-job-name my-first-transcription-job \ --media MediaFileUri=s3://DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET/my-input-files/my-media-file.flac \ --output-bucket-name DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET \ --output-key my-output-files/ \ --language-code en-US \ --show-speaker-labels TRUE \ --max-speaker-labels 3Here's another example using the start-transcription-job command, and a request body that enables speaker partitioning with that job.
aws transcribe start-transcription-job \ --region us-west-2 \ --cli-input-json file://my-first-transcription-job.jsonThe file my-first-transcription-job.json contains the following request body.
"TranscriptionJobName": "my-first-transcription-job", "Media": "MediaFileUri": "s3://DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET/my-input-files/my-media-file.flac" >, "OutputBucketName": "DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET", "OutputKey": "my-output-files/", "LanguageCode": "en-US", "ShowSpeakerLabels": 'TRUE', "MaxSpeakerLabels": 3 >This example uses the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3) to identify channels using the start_transcription_job method. For more information, see StartTranscriptionJob.
from __future__ import print_function import time import boto3 transcribe = boto3.client('transcribe', '" job_uri replaceable">DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET/us-west-2') job_name replaceable">my-first-transcription-jobmy-input-files/my-media-file.flac" transcribe.start_transcription_job( TranscriptionJobName = job_name, Media = 'MediaFileUri': job_uri >, OutputBucketName = 'DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET', OutputKey = 'my-output-files/', LanguageCode = 'en-US', Settings = 'ShowSpeakerLabels': True, 'MaxSpeakerLabels':3> ) while True: status = transcribe.get_transcription_job(TranscriptionJobName = job_name) if status['TranscriptionJob']['TranscriptionJobStatus'] in ['COMPLETED', 'FAILED']: break print("Not ready yet. ") time.sleep(5) print(status)
To partition speakers in a streaming transcription, see the following examples:
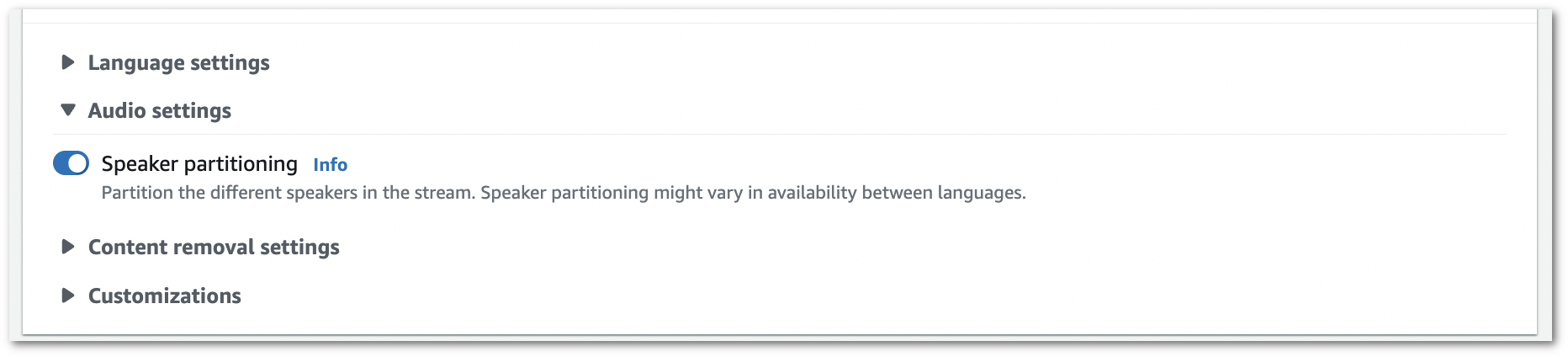
This example creates an HTTP/2 request that partitions speakers in your transcription output. For more information on using HTTP/2 streaming with Amazon Transcribe, see Setting up an HTTP/2 stream. For more detail on parameters and headers specific to Amazon Transcribe, see StartStreamTranscription.
POST /stream-transcription HTTP/2 host: transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com X-Amz-Target: com.amazonaws.transcribe.Transcribe.StartStreamTranscription Content-Type: application/vnd.amazon.eventstream X-Amz-Content-Sha256: string X-Amz-Date: 20220208T235959Z Authorization: AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=access-key/20220208/us-west-2/transcribe/aws4_request, SignedHeaders=content-type;host;x-amz-content-sha256;x-amz-date;x-amz-target;x-amz-security-token, Signature=string x-amzn-transcribe-language-code: en-US x-amzn-transcribe-media-encoding: flac x-amzn-transcribe-sample-rate: 16000 x-amzn-transcribe-show-speaker-label: true transfer-encoding: chunkedParameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.
This example creates a presigned URL that separates speakers in your transcription output. Line breaks have been added for readability. For more information on using WebSocket streams with Amazon Transcribe, see Setting up a WebSocket stream. For more detail on parameters, see StartStreamTranscription .
GET wss://transcribestreaming.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:8443/stream-transcription-websocket? &X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 &X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE%2F20220208%2Fus-west-2%2Ftranscribe%2Faws4_request &X-Amz-Date=20220208T235959Z &X-Amz-Expires=300 &X-Amz-Security-Token=security-token &X-Amz-Signature=string &X-Amz-SignedHeaders=content-type%3Bhost%3Bx-amz-date &language-code=en-US &specialty=PRIMARYCARE &type=DICTATION &media-encoding=flac &sample-rate=16000 &show-speaker-label=trueParameter definitions can be found in the API Reference; parameters common to all AWS API operations are listed in the Common Parameters section.